6 Reasons WI-FI Drops
1
Wi-Fi Radio Interference
Radio signals from various consumer electronic products can interfere with Wi-Fi wireless network signals. For example, cordless phones, Bluetooth devices, garage door openers and microwave ovens can each take down a Wi-Fi network connection when powered on. You can move your network equipment or (on home networks) change some Wi-Fi radio settings to avoid this problem.2
Insufficient Wi-Fi Network Range and Power
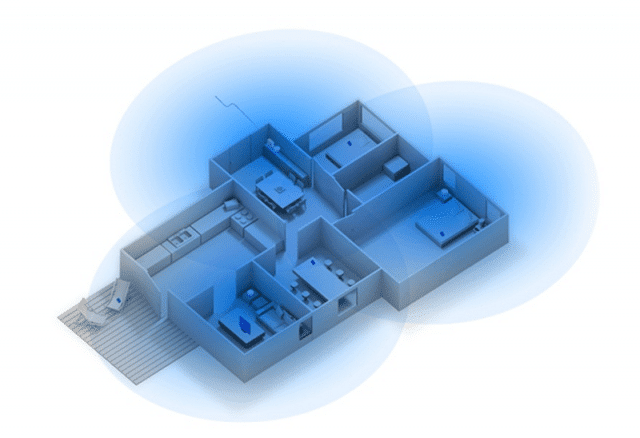
Even without interference from other equipment, Wi-Fi connections can drop occasionally on devices located near the edge of the network’s wireless signal range. Wi-Fi links generally become more unstable with distance. Relocating your computer or other gear is a simple but not always practical solution. Otherwise, consider antenna upgrades and other techniques to improve wireless signal transmission and reception.Solution: Position Your Router / Access Point for Best Performance
3
Unknowingly Connecting to the Wrong Wi-Fi Network
If two neighboring locations run unsecured Wi-Fi networks with the same name (SSID), your devices may connect to the wrong network without your knowledge. This can cause the interference and range problems described above. Additionally, in this scenario your computers will lose connection whenever the neighbor network is turned off, even if your preferred one remains functional. Take proper security measures to ensure your computers connect to the right network.4
Network Driver or Firmware Upgrade Required
Each computer connected to a Wi-Fi network utilizes a small piece of software called the device driver. The Wi-Fi network device driver controls various functions of the Wi-Fi hardware. Network routers contain related technology called firmware. Network drivers and firmware can both become obsolete over time. Upgrading (over installing) newer versions of these things can sometimes fix network connection problems. Get free upgrades from the manufacturer’s Web sites.5
Incompatible Software Packages Installed
Wi-Fi network connections may start failing on a computer due to incompatible software installed and running there. This includes operating system patches, operating system services, and other software that modifies the networking capabilities of the operating system. Keep records of each time you install or upgrade software on your computers, and be prepared to uninstall any incompatible software you’ve added recently.6